
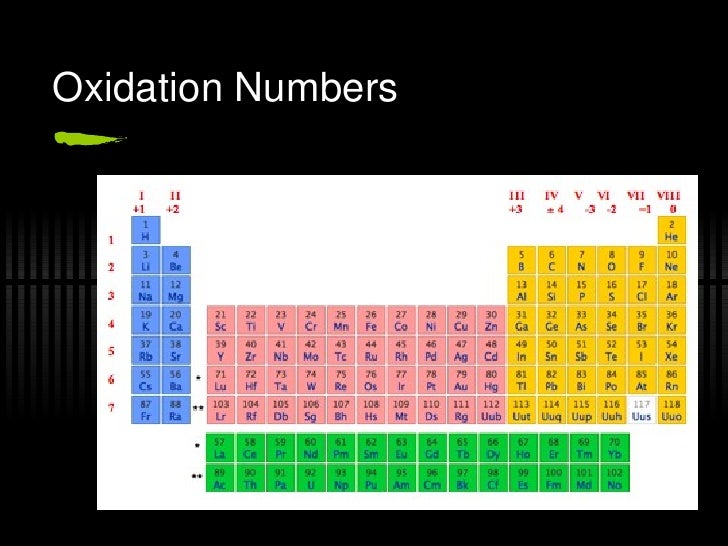
A common oxidation state is an oxidation state that you are most likely to see the ion has in a ion or a compound. Although the chemistry of d-block elements is complex, the reason for the two differently charged ions has to do with the number of valence electrons in the outer shell and how they fill the d-subshell.Ĭertain atoms have ions with a common oxidation state. At GCSE you probably learned that iron has two ions, one with a +2 charge and one with a +3 charge. Oxidation states are used to determine the degree of oxidation or reduction that an element has undergone when bonding. Chemistry Periodic Table oxidation numbers. The other elements that have a variable oxidation state are the d-block elements. It also has a low ionisation energy and a large atomic radius which means that it can easily lose electrons to another atom in a bond giving it an oxidation state of up to +7.

The reason for this is because chlorine has a high electronegativity value which means that it can attract an electron to itself in a bond causing the oxidation state of -1. Or it can lose seven valence electrons to have an oxidation state of +7. First I explain what oxidation numbers tell us. So, it can either gain one valence electron to complete its shell and have an oxidation state of -1. In this video, we start looking at oxidation numbers (which are also called oxidation states). The reason for this is that the chlorine atom has seven valence electrons in its outer shell. It is because the stock notation of oxidation numbers is the basis of the periodic property, electronegativity. Chlorine has several oxidation states which vary from -1 to +7. The oxidation number is frequently used interchangeably with an Oxidation state. The number of valence electrons of elements increases and ranges between 1 and 8 while travelling left to.

A variable oxidation state means that the oxidation state of an atom depends on what it is bonded to in the compound or ion.Īt GCSE you probably learned that the halogens have a charge of -1. Periodic Trends in the Oxidation States of Elements. The nonmetals have a variable oxidation state. Using this logic, magnesium has an oxidation state of +2 and aluminium has an oxidation state of +3. It can't have an oxidation state of +2 because it only has one valance electron in it's outer shell. Sodium has an oxidation state of +1, The reason it has this oxidation states is that it equals the number of valance electrons in the outer shell of the atom. This means that the oxidation state doesn't change even though what it is bonded to in a compound or ion may change. Group 1, 2 and 3 atoms all have fixed oxidation states. However, if you use the term oxidation state when referring to the charge on the ion then redox equations will make a lot more sense. The two terms can be used interchangeably. The oxidation number describes explicitly the degree to which an element can be oxidized (lose electrons) or reduced(gain electrons). The oxidation state of ion in A-level is the same as the charge on the ion in GCSE.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
